|

|
Inhalational Anesthetic Agents
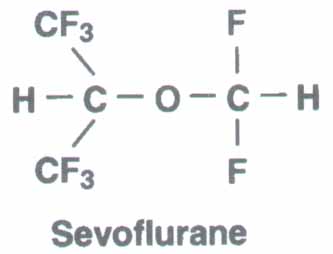
Sevoflurane, (CF3)2-CH-O-CFH2
Relatively low solubility and nonpungency make it an excellent choice for inhalational induction.
Physical Properties
- vapor pressure = 160 mmHg at 20 deg C
- low solubility (lambdablood:gas = 0.65)
- moderate vapor pressure (160 mmHg at 20 degrees C)
Organ System Effects
Cardiovascular
- mild negative inotrope
- little or no tachycardia
- so cardiac output not as well maintained as with isoflurane or desflurane
- may prolong the QT interval
Respiratory
- depresses respiration
- bronchodilator
CNS
- general anesthesia, MAC = 2.0
- slightly increases CBF and ICP
- decreases CMRO2
Biotransformation and Toxicity
- rate of metabolism = 5% (ten times that of isoflurane)
- inorganic fluoride is a metabolic product
soda lime (NOT calcium hydroxide) degrades sevoflurane to compound A
- nephrotoxic in rats
- accumulation of compound A increases with
- increased respiratory gas temperature
- low-flow anesthesia
- dry barium hydroxide absorbent
- high sevoflurane concentrations
- time
- some recommend minimum total fresh gas flows of 2 L/min and
- avoid if preexisting renal dysfunction
- metal and environmental impurities can degrade sevoflurane to hydrogen fluoride
- can produce acid burn of respiratory mucosa
- degradation minimized by adding water during manufacture and packaging in special plastic containers
Contraindications


|