Inhalational Anesthetic Agents
Enflurane, CFClH-CF2-O-CF2H
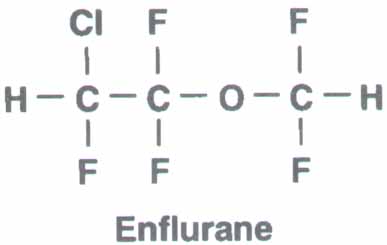
Introduced in 1972.
Physical Properties
- vapor pressure = 175 mmHg at 20 deg C
- halogenated ether
- mild, sweet,ethereal oder
Organ System Effects
Cardiovascular- negative cardiac inotrope
- lowers cardiac output, arterial blood pressure, myocardial oxygen consumption
- heart rate usual increases
- rapid, shallow breathing with increased paCO2
- abolishes hypoxic drive
- bronchodilator
- depresses mucocillary function
- marked respiratory depression so that at 1 MAC, paCO2 = 60 mmHg
- general anesthesia, MAC = 1.7
- increases CBF and ICP
- increases CSF secretion
- deep enflurane aneshthesia -> EEG spike-and-wave pattern -> tonic-clonic seizures, exacerbated by hypocapnia (so hyperventilation not recommended)
- decreases CMRO2 (unless seizures occur)
Biotransformation and Toxicity
- fluoride is produced but even after 10 MAC-hours average concentrations are < 40 micromols/L
- causing mild reduction in renal concentrating ability
Contraindications/Precautions
- malignant hyperthermia susceptibility
- preexisting kidney disease
- seizure disorder
- intracranial hypertension
- isoniazid enhances enflurane defluorination