Inhalational Anesthetic Agents
Desflurane, CF3-CFH-O-CF2H
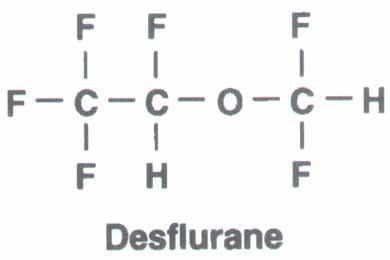
Introduced in 1992.
Physical Properties
- vapor pressure = 681 mmHg at 20 degrees C so
- boils at room temperature at high altitudes (eg, Denver, Colorado), and
- requires special vaporizer
- low solubility permits rapid changes in pA and thus pBrain
- pungent and irritating to the airway
Organ System Effects
Cardiovascular- similar to isoflurane (but does NOT increase coronary artery blood flow)
- cardiac output no more than slightly depressed at 1-2 MAC
- rapid increases in pa may -> pronounced tachycardia and hypertension
- fast, shallow breathing with incresased paCO2
- airway irritation
- salivation
- breath-holding
- coughing
- laryngospasm
- general anesthesia, MAC = 6.0
- cerebral vasodilator, increases CBF and ICP
- marked decrease in CMRO2 tends to cause compensatory vasoconstriction
- EEG effects similar to isoflurane
Biotransformation and Toxicity
- minimal metabolism in vivo
- degraded (more than other agents) to potentially harmful levels of carbon monoxide
by desiccated carbon dioxide absorbent
- especially by barium hydroxide lime, but also by sodium and potassium hydroxide
- use of calcium hydroxide minimizes this degradation problem
Contraindications
- malignant hyperthermia susceptibility
- hypovolemia
- intracranial hypertension